The Trustless Manifesto: Why THORChain Is Structurally Different

Vitalik Buterin’s recent publication, The Trustless Manifesto, highlights a growing structural risk across the crypto ecosystem. His central point is that the industry is drifting toward reliance on intermediaries. The shift is gradual, often framed as a UX improvement, and increasingly treated as normal. As Buterin warns:

The risks Vitalik describes are already embedded in the design of most L1s, L2s, and cross-chain systems. Centralised sequencers, hosted RPCs, privileged relayers, and upgrade keys have become normalised across the ecosystem, concentrating influence among a small set of operators.
👉 THORChain chose a different path from the start.
It treated trust-minimisation as a requirement rather than a future milestone. Several of the failure modes called out in the Trustless Manifesto were anticipated and intentionally avoided at the protocol level.
This article examines how THORChain’s architecture positions it as a leader in credible neutrality, rather than a participant in the industry’s broader drift toward trust-based infrastructure.
Cross-Chain Without Relayers: Trustless Interoperability by Default
In the Trustless Manifesto, Buterin warns that interoperability layers are increasingly replicating the centralisation problems they were meant to overcome. He writes:

This criticism reflects a structural flaw in most bridging protocols. Cross-chain messaging and asset transfer often rely on relayer networks or external validators to observe events on one chain and trigger corresponding actions on another.
These actors function as gatekeepers, determining which transactions are valid, in what order they are processed, and whether they are forwarded at all. In many cases, these intermediaries operate through privileged roles, proprietary APIs, or multisig-controlled contracts. If these actors are compromised or censored, the bridge becomes unusable.
👉 THORChain avoids this failure mode entirely. Its architecture enables native asset swaps, not through wrapping, pegging, or external validation, but through protocol-enforced observation and distributed key management.
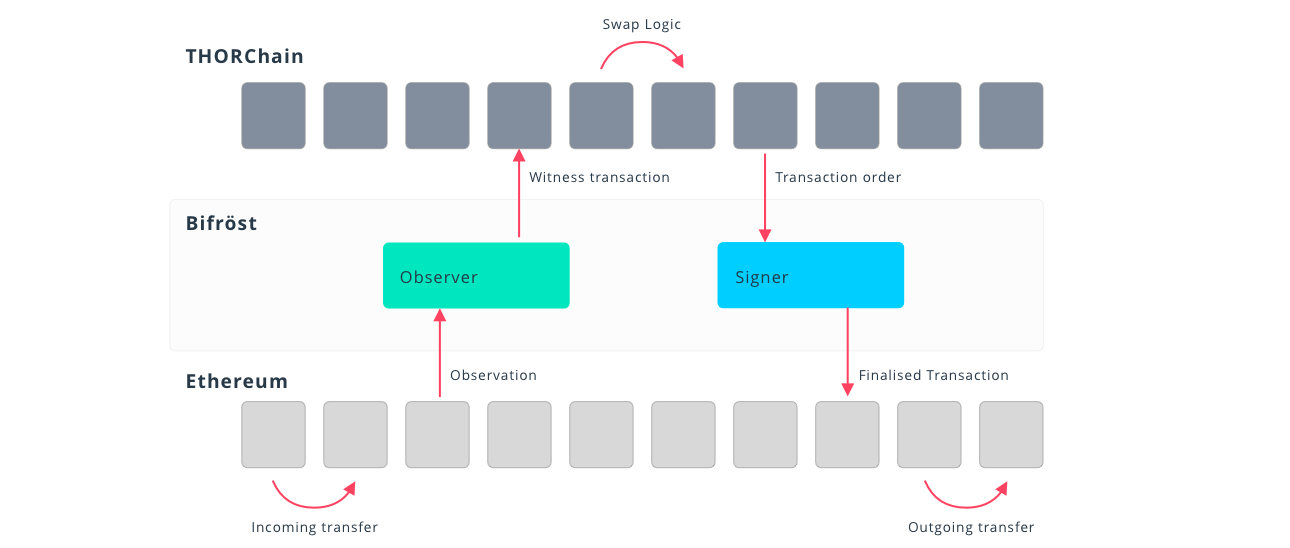
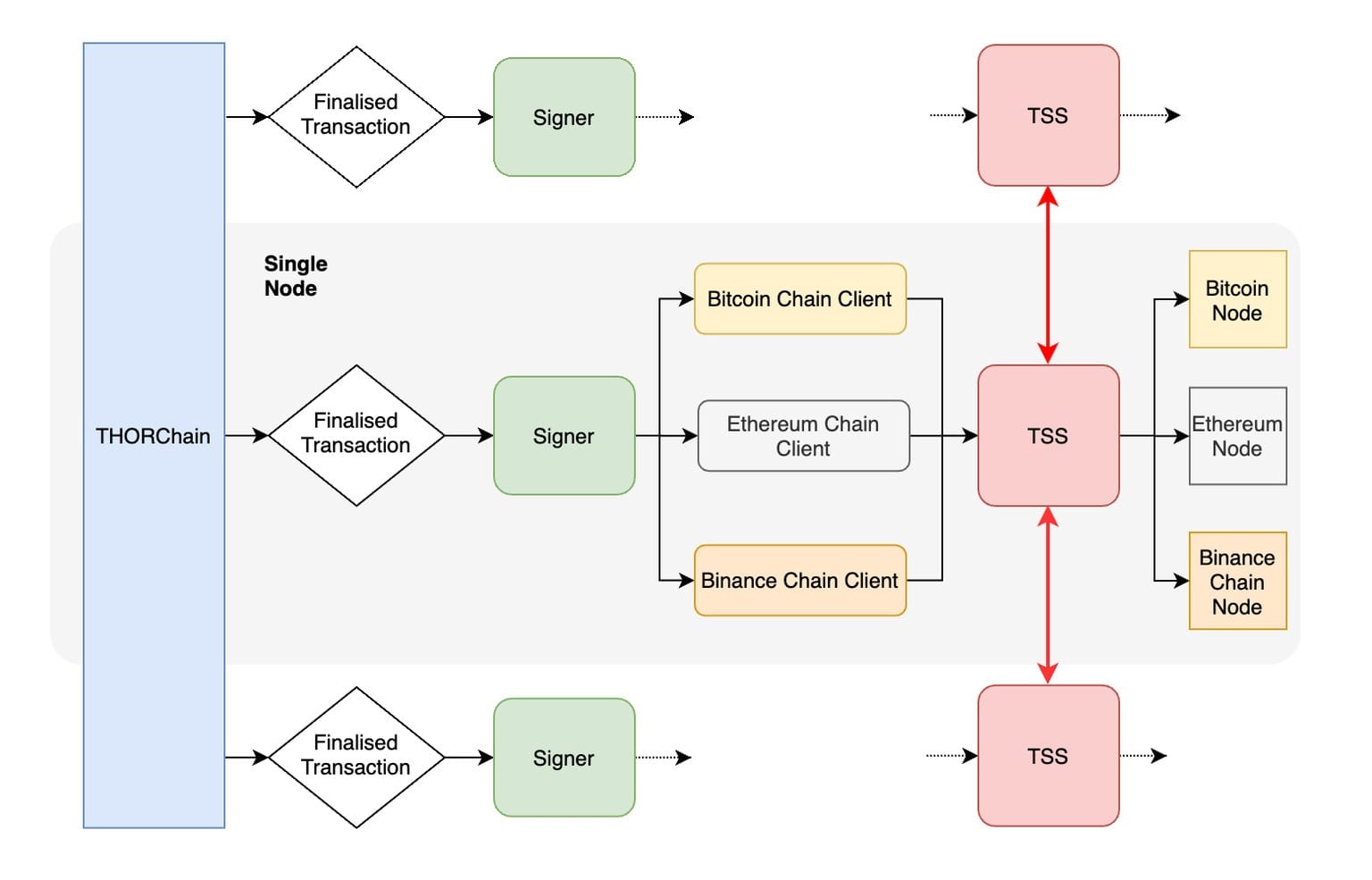
Each THORNode independently runs Bifröst modules that watch inbound transactions on external chains such as Bitcoin or Ethereum. Once the required threshold of nodes sees a transaction, consensus is reached via Tendermint, and the outbound leg of the swap is executed using a Threshold Signature Scheme (TSS) with no single point of failure.
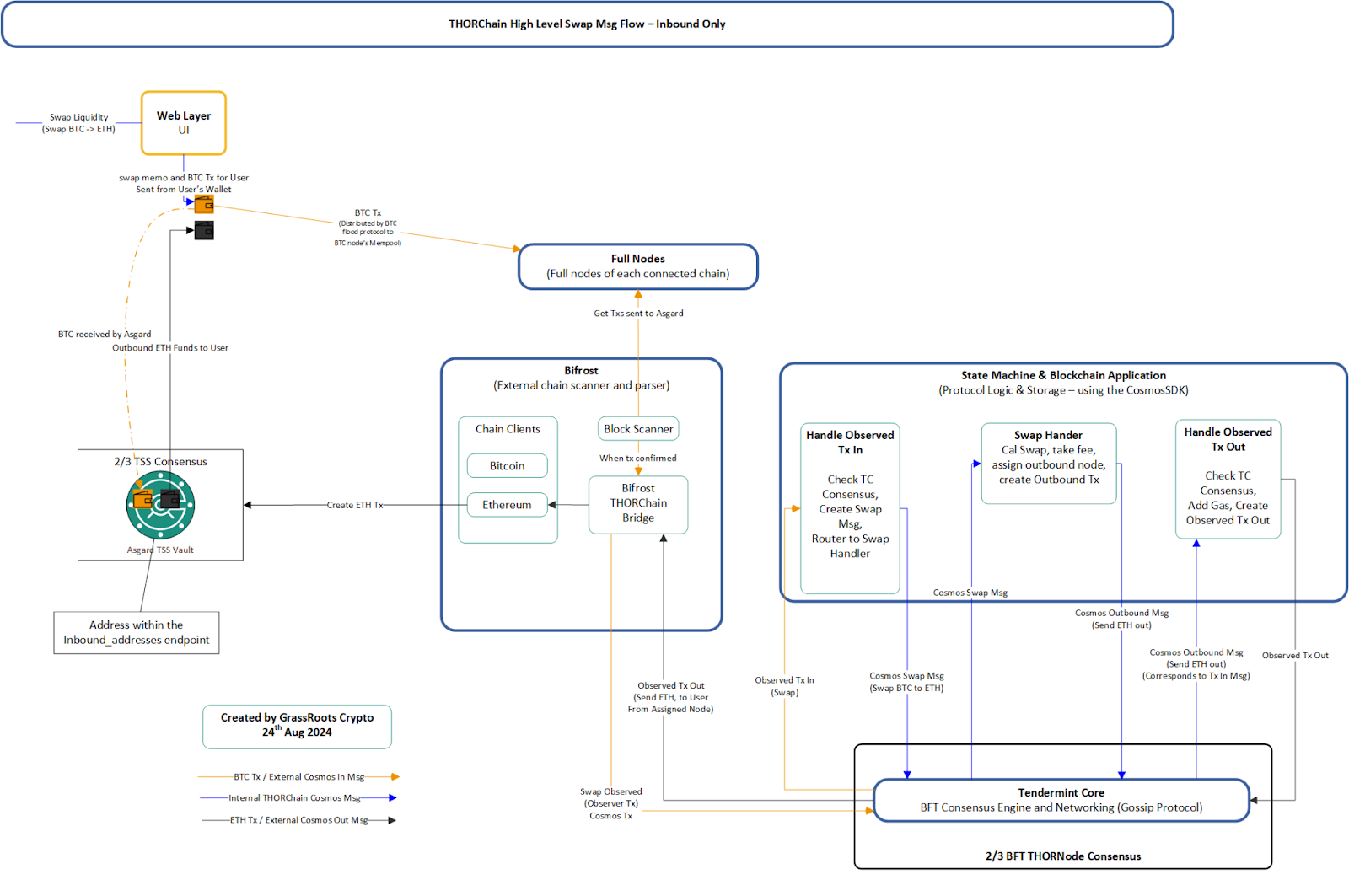
There are no external relayers to trust, no synthetic assets to custody, and no messaging layer that controls execution.
On the first point raised in the Trustless Manifesto, we can clearly see how THORChain takes a different approach. While many cross-chain systems rely on relayers or wrapped assets, THORChain handles native asset swaps entirely through its own validator set and on-chain logic.
Each transaction is processed using public data and network consensus, with no single party in control. This design removes the need for trusted intermediaries and shows that trustless cross-chain execution is not only possible, but already functioning reliably in production.
Validator Set Design: Replaceability, Rotation, and Practical Openness
The Trustless Manifesto repeatedly emphasises the difference between theoretical openness and actual accessibility. It states:

In many proof-of-stake chains, validator participation is open in theory but constrained in practice. Entry is often bottlenecked by high hardware demands, large capital requirements, complex tooling, or validator delegation models that favor early insiders. Many networks maintain upgrade rights or critical governance levers through foundations, working groups, or multisigs, which undermines the neutrality of the infrastructure.
👉THORChain addresses this challenge through a combination of technical and economic constraints.
First, bonding requirements are capped to prevent individual validators from dominating the network. Second, the active validator set is rotated every few days using a process called churn. Older or lower-bonded nodes are removed and replaced with new entrants.
This process is automatic, consensus-driven, and not subject to manual coordination or privileged approval. Finally, protocol governance is handled entirely on-chain by the validator set. There are no upgrade keys or emergency levers held by any team, foundation, or multisig.
For further detail, Grassroot’s explanatory video is available here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XXYXNAolPEU
Transparent Execution and Verifiability: Eliminating Hidden State and Private Logic
Another foundational argument in the Trustless Manifesto is that correctness must be independently verifiable. The authors write:

In many modern systems, frontends are open while key logic is moved off-chain or routed through APIs that are not public or reproducible. Pricing mechanisms, liquidity routing, transaction batching, and even inclusion policies are often controlled by hidden services.
👉 THORChain avoids this design pattern by keeping its core logic inside the protocol itself and making all state changes visible on-chain.
Swaps happen through native liquidity pools that use simple maths based on the balances in each pool to determine prices. No hidden services are deciding how a trade should be priced or routed. Everything is calculated from information that any user can see.
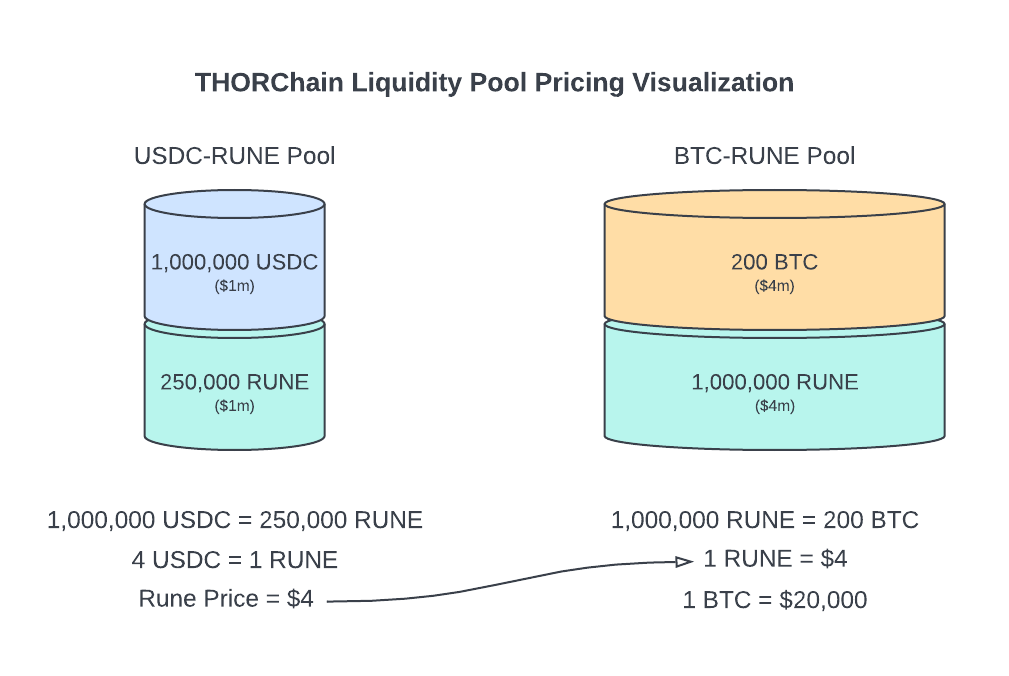
The logic for calculating price impact, slippage, and fees is transparent, auditable, and based solely on pool balances. Execution ordering is determined by a price-impact-based queue that limits frontrunning and reduces opportunities for extractive behaviour. No private routing or dynamic pricing logic is applied.
Custody is handled by threshold signature vaults controlled by the active validator set. A supermajority of nodes must approve outbound transactions, and the history of vault activity is visible on-chain. The state of all vaults, liquidity pools, and validator bonds is publicly accessible and updated with every block.
Protocol incentives and behaviour are also transparent. The Incentive Pendulum automatically adjusts reward distribution between validators and liquidity providers based on network conditions.
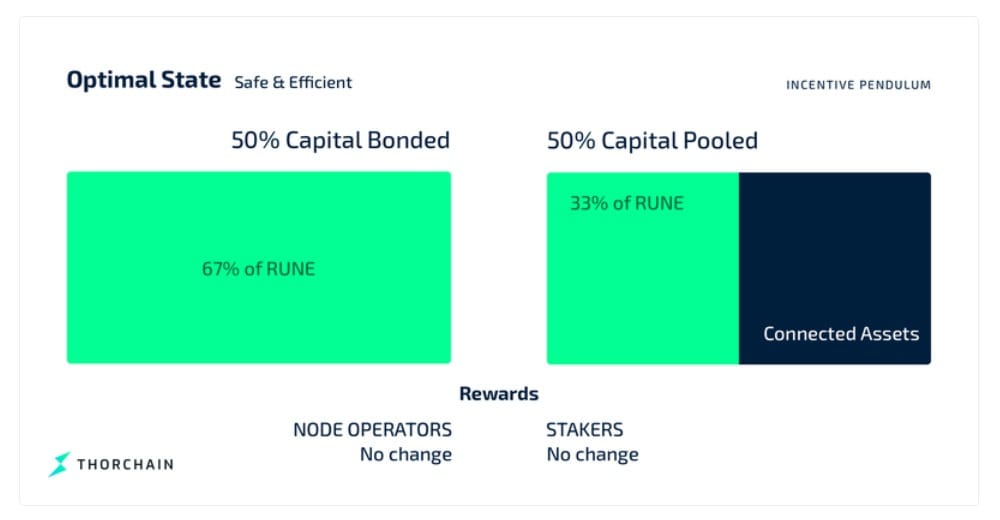
These adjustments are driven by metrics encoded in the protocol itself, not by external decision-making. Governance proposals, parameter changes, and chain-level updates are handled on-chain through validator voting, with no administrative override mechanism.
All of THORChain’s code is open source. Anyone can run a node, replay the chain, and verify that the current state aligns with the expected outcome based on public inputs and rules. Participants do not need to trust a centralised team, off-chain service, or opaque backend process. They interact with a system where fairness and correctness are enforced through protocol logic and consensus.
This aligns closely with the Manifesto’s requirement for verifiability. Users and participants are not expected to trust the intentions of validators or developers. They can inspect and confirm outcomes independently using the same protocol rules that govern the system.
Conclusion: THORChain as a Practical Example of Trustlessness
The Trustless Manifesto highlights six essential qualities of a trustless system. A protocol must allow users to act for themselves, verify outcomes from public data, resist censorship, replace any operator who leaves or misbehaves, remain accessible in practice, and make incentives fully transparent. These are not optional features.

They are the baseline requirements for systems that aim to remove dependence on intermediaries.
👉 THORChain meets these requirements through its native asset pools, open validator design, public state transitions, and on-chain governance. Users initiate every action directly. All activity can be inspected from the chain.
Validators can enter or exit without permission, and the network keeps functioning when they do. Incentives and rules are encoded in the protocol, not controlled off-chain.
For readers of this blog, the message is simple. THORChain does not just agree with the principles laid out in the Trustless Manifesto. It demonstrates them.
While much of the industry is drifting toward convenience-first designs that rely on trusted infrastructure, THORChain continues to show what fully trustless architecture looks like in production. It is a working example of the standards the Manifesto calls for, and it sets a clear path forward for how cross-chain systems can be built without compromising on trustlessness.



